مدونة
A Cardiovascular Disease-Linked Gut Microbial Metabolite Acts via Adrenergic Receptors
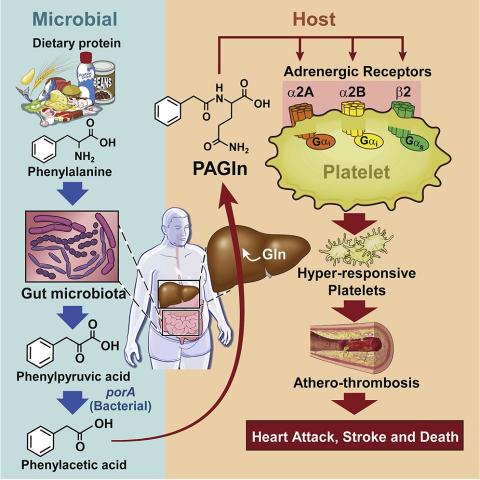
•Gut microbe formed phenylacetyl glutamine (PAGln) contributes to cardiac disease
•Microbial porA and fldH impact host PAGln levels, platelet function, and thrombosis
•PAGln transmits cellular responses via the α2A, α2B, and β2 adrenergic receptors
•β blocker therapy attenuates PAGln-induced heightened thrombosis risk

